
Non-Americans often refer to the standard form in math in connection with a very different topic. Therefore, when we convert to standard form, it's all about choosing the power of 10 in such a way so that the b in the formula is between 1 and 10.Īlright, after all this time learning the theory, it's finally time we saw some standard form examples, wouldn't you say? The absolute value of the standard form exponents n tell us how many places we have to move the point, and the sign of n indicates if it should be to the right (for n positive) or the left (for n negative). To sum up, in the standard form math formula Which is the value we had but with the point one place to the left. This movement by 2 is shown by the power in the standard form exponents.Ĭonversely, if we divide the initial number by 10, which is equal to multiplying it by 1/10 = 10⁻¹, we'll get Which is the number we had initially but with the point two places to the right. In other words, we move the point one place to the right. If we take a number, say, 12,345.6789, and multiply it by 10, we'll get And that is exactly what the standard form exponents are for. , that separates the digits of the number by one place, which is equivalent to 10 to the power of one. What we've done above is basically move the point. We could, however, convert it to standard form by saying that This means that, for example, 1.36 × 10⁷ or 9.81 × 10⁻²³ are in standard form, but 13.1 × 10¹² isn't because 13.1 is bigger than 10.

We said that the number b should be between 1 and 10. Now, back to the question of the hour, "What does standard form mean?"īefore we give some examples of writing numbers in standard form in physics or chemistry, let's recall from the above section the standard form math formula: In that case, check out our quadratic formula calculator, but be sure to come back to us whenever you get the chance! Warning: There is a possibility that you've come across this standard form calculator in search of different ways of writing a quadratic equation. Also, note how you can switch between the two variants in the advanced section by choosing the appropriate option in the field " Have the calculator use." This notion is connected to the expanded form, and we explain it all in detail in the dedicated section. Outside of the USA (especially in the UK), we say that a number is in its standard form if it's a single value that involves no arithmetic operations whatsoever. That's why we made this standard form converter - to help you with just that.įor our non-American friends out there, the standard form is usually a quite different thing. Preferably, we can use standard form exponents and write the same thing with just a few symbols. It's quite troublesome to write all the zeros of a number in every line of our calculations. But let's just say that standard form in math and physics (quite often called scientific notation) is a neat way of dealing with very large or very small values. "What is the standard form?" Well, we'll get to the standard form definition soon enough.
Factor form to standard calculator how to#
Here are the search phrases that today's searchers used to find our site.Welcome to the standard form calculator, where we'll learn how to write a number in standard form.
Factor form to standard calculator software#
Students struggling with all kinds of algebra problems find out that our software is a life-saver. Also, thank you for not using the new new software as an excuse to jack up the price. With your new WYSIWYG interface that problem has been completely eliminated! It's like Word Equation Editor, just simpler. I found the old Algebrator useful, but it was really difficult to enter more complex expression. R.B., KentuckyĪs a user of both Algebrator 2.0 and 3.0 I have to say that the difference is incredible. I'm so impressed with it! I can't stress enough how great it is! Zoraya ChristiansenĪ solid software and we need more like it. I eventually got tired of her so I decided to try the software. My former algebra tutor got impatient whenever I couldn't figure out an equation.

Subtracting Rational Expressions with the Same DenominatorĪxis of Symmetry and Vertex of a Parabola Simplifying Products and Quotients Involving Square RootsĪdding Rational Expressions with the Same DenominatorĪdding, Subtracting and Multiplying Polynomials Simplifying Square Roots That Contain Variables Quadratic Equations with Imaginary SolutionsĪdding and Subtracting Rational Expressions With Different Denominators Solving Quadratic Equations by Completing the SquareĪdding and Subtracting Rational Expressions with Unlike Denominators Simplifying Square Roots That Contain Whole Numbers
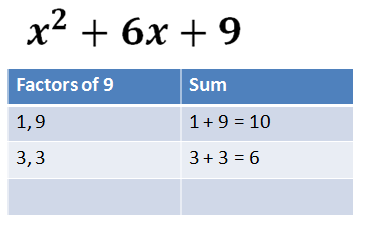
Systems of Equations That Have No Solution or Infinitely Many Solutionsĭividing Polynomials by Monomials and Binomials Solving Linear Systems of Equations by Elimination Solving Quadratic Equations by Using the Quadratic Formula


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
